test for tibial torsion|tibial torsion in adults : solutions Tibial torsion is the twisting of a child’s shinbone, also known as the tibia. In most cases, tibial torsion causes a toddler’s legs and feet to turn inward (internal tibial torsion), giving them a pigeon-toed appearance. Less often, the legs turn . Uma investigação da BBC descobriu que fotos íntimas de mulheres e meninas estão sendo compartilhadas em grupos com dezenas de milhares de usuários no aplicativo de mídia .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBUnilabs Santa Maria da Feira em Santa Maria da Feira | 14 comentários | número de telefone. Accueil. Santa Maria da Feira. Clínica Médica. Unilabs Santa Maria da Feira. .
Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle > 10 degrees of .
Tibial torsion is the twisting of a child’s shinbone, also known as the tibia. In most cases, tibial torsion causes a toddler’s legs and feet to turn inward (internal tibial torsion), giving them a pigeon-toed appearance. Less often, the legs turn .
tibial torsion special test
tibial torsion in adults
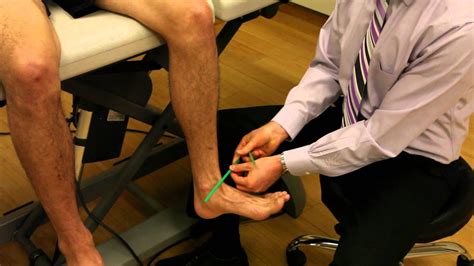
Dr. Rome explains how to look for tibial torsion, or tibial rotation, with the knee at a 90 degree angle. External Tibial Torsion is a rare developmental condition in young children caused by abnormal external rotation of the tibia leading to an out-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle measuring greater .The diagnosis of tibial torsion is made by a history and physical examination by your child's doctor. During the examination, the doctor obtains a complete prenatal and birth history of the . Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of in-toeing. It is usually seen at age 2 years. Males and females are affected equally, .
Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. This condition causes a child to have inward-facing toes and bowed legs. It may be caused by the position of the baby in the uterus. A physical exam can diagnose tibial torsion. .To evaluate for tibial torsion, the angle between the axis of the foot and the axis of the thigh is measured with the child prone and the knees flexed to 90 °. Typically the foot axis is 10 ° .To evaluate for tibial torsion, the angle between the axis of the foot and the axis of the thigh is measured with the child prone and the knees flexed to 90°. Typically the foot axis is 10° .Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shin bones (the bones that are located between the knee and the ankle). Tibial torsion causes the child's feet to turn inward, or have what is also known as a "pigeon-toed" appearance. It is typically seen among toddlers. What causes tibial torsion? Tibial torsion can occur due to the position of the .
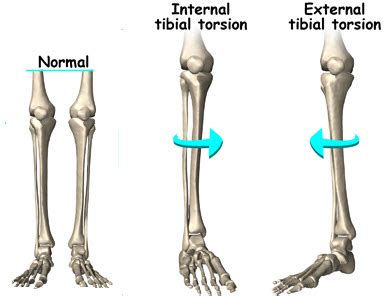
Internal tibial torsion can be diagnosed through a physical exam and measurements of the legs. Internal Tibial Torsion Treatment. This condition usually improves without treatment by about 4 years of age. Bracing, casting and physical therapy are not usually needed. A child’s growth is closely monitored to ensure the internal tibial torsion . Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of in-toeing. It is usually seen at age 2 years. Males and females are affected equally, and about two thirds of patients are affected bilaterally. [1, 2] Tibial torsion can persist into adulthood and give rise to patellofemoral pathology.Tibial torsion can be external (lateral) or internal (medial). (See also Introduction to Congenital Craniofacial and Musculoskeletal Disorders.) External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically .
Tibial Torsion What is tibial torsion in children? Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. Tibial torsion causes a child’s feet to turn inward. . Know why a test or procedure .In the measurements using the new method, tibial torsion values at first measurement made by four trained physicians were 35 ± 8.6° (range 16–70°), and for the next month measurements it was 35.2 ± 9.1° (range 6–71.5°) ().Analysis of variance between all measurement sessions with the two techniques of measurement did not show any significant difference, so it can be . Tibial torsion test in sitting position. Tibial torsion is measured by having the patient sit with the knee flexed to 90’over the edge of the examining table. The examiner has put the thumb of one hand over the apex of the one malleolus. Next, the examiner visualizes the axes of the knee & of the ankle.
Tibial torsion was calculated by subtracting the proximal tibial angle from the distal tibial angle. . Continuous variables were checked for normal distribution using the Shapiro–Wilk test, and presented in the form of mean ± SD (standard deviation). Statistical significance was evaluated between different groups using the paired t test. Tibial torsion is a twist in the tibia measured as an angle between a proximal axis line and a distal axis line. Abnormal torsion has been associated with a variety of painful clinical syndromes of the lower limb. . samples and 3 raters were used for the reliability study. 21 Data were assessed for normality using a Shapiro-Wilk test .By mid-childhood, a small percentage of children will continue to have significant tibial torsion. How is tibial torsion diagnosed? Tibial torsion is diagnosed (and distinguished from other causes of in-toeing) by a careful physical exam. Tibial torsion is assessed by measuring the thigh-foot angle, if the foot is shaped normally. knee pain when associated with tibial torsion. awkward running style. . trochanteric prominence angle test . patella internally rotated on gait evaluation. tibial torsion. look at thigh-foot angle in prone position. normal value in infants- .
physical therapy for tibial torsion
Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. Tibial torsion causes a child's feet to turn inward. . Know what to expect if your child does not take the medicine or have the test or procedure. If your child has a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for .Tibial torsion occurs if the child's lower leg (tibia) twists inward. This can occur before birth, as the legs rotate to fit in the confined (limited) space of the womb. After birth, an infant's legs should gradually rotate to align properly. If the lower leg remains turned in, the result is tibial torsion. What causes tibial torsion? Tibial torsion tends to be hereditary and can be passed down from parents to children. The position of a fetus in the uterus can also make a child more likely to have tibial torsion. What are the symptoms of tibial torsion? The "in-toeing", or walking with the toes pointed inward, is the primary symptom of tibial . An initial screening test for tibial torsion can be performed with the patient supine. Hip internal and external rotation is first examined in 90° of hip flexion and then in neutral flexion (0 degrees) with the foot perpendicular to the ground. In 90° of flexion, the internal and external rotations should be symmetrical, while in neutral, the .
Internal tibial torsion is one cause of intoeing. With internal tibial torsion, the shin bone (tibia) is slightly twisted or rotated, causing the foot to turn in. This may be due to the position your child was sitting in while in the uterus. Intoeing due . External Tibial Torsion: - Knees face outward, often leading to a wider stance. - This places extra stress on the outer knee and hips. - Squat depth and stability are compromised due to improper muscle loading. Lunging with Tibial Torsion. Lunges demand stability and alignment, both of which are challenged by tibial torsion: Internal Tibial .
Physical exam test procedure for examination of the foot and ankle and associated structures.
Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. Craig's test is described in detail here. . Thigh-foot angle (TFA): a means to measure tibial torsion. To measure internal or external tibial torsion, the patient is positioned in prone lying with their knees flexed to 90° and . Femoral and tibial torsion were measured by both EOS imaging and three-dimensional computed tomography (3D CT) reconstruction. Bland-Altman plots were performed to evaluate the difference between femoral and tibial torsion measurements obtained by these two methods. The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to evaluate intrareader . Physical examinations of tibial torsion are used for preoperative planning and to assess outcomes of tibial osteomy in patients with cerebral palsy (CP). . it is important to confirm a physical examination is as valid and reliable as an imaging study and which test is superior in determining tibial torsion. The aim of this study was to .External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically resolves with growth. However, an excessive degree of torsion may indicate a neuromuscular problem. Torsion also occurs with Blount disease. Persistent .
Standard radiographs of the knee can show several findings suggestive of acute PLC injury, including abnormal widening of the lateral joint space, fibular tip avulsion fracture or fracture of the fibular head, avulsion fracture off Gerdy’s tubercle in iliotibial band injuries, tibial plateau fracture, or even a Segond fracture. Tibial neuropathy refers to any dysfunction of the tibial nerve. The most common known association is tarsal tunnel syndrome, which is tibial neuropathy as it crosses through the tarsal tunnel at the level of the ankle. Although tarsal tunnel syndrome and tibial neuropathy can be used synonymously, they represent separate entities.Background Quantifying femoral and tibial torsion is crucial in the preoperative planning for derotation surgery in children and adolescents. The use of an ultra-low-dose computed tomography (CT .
Tibial Torsion in Children What is tibial torsion in children? Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. Tibial torsion causes a child’s feet to turn inward. . Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.
internal tibial torsion in adults
how to measure tibial torsion
how to correct tibial torsion
how to assess tibial torsion
WEBNós TWA hae prazo aboot os braes. We twa hae run aboot the braes. E pu'd os gowans fina. And pu'd the gowans fine. Nós temos mony vagueado um pé cansado. We've .
test for tibial torsion|tibial torsion in adults